Western Steel's
Hybrid Steel Building System
Our Hybrid Buildings incorporate both conventional steel primary members and pre-engineered secondary members, bringing the best qualities of each, together.
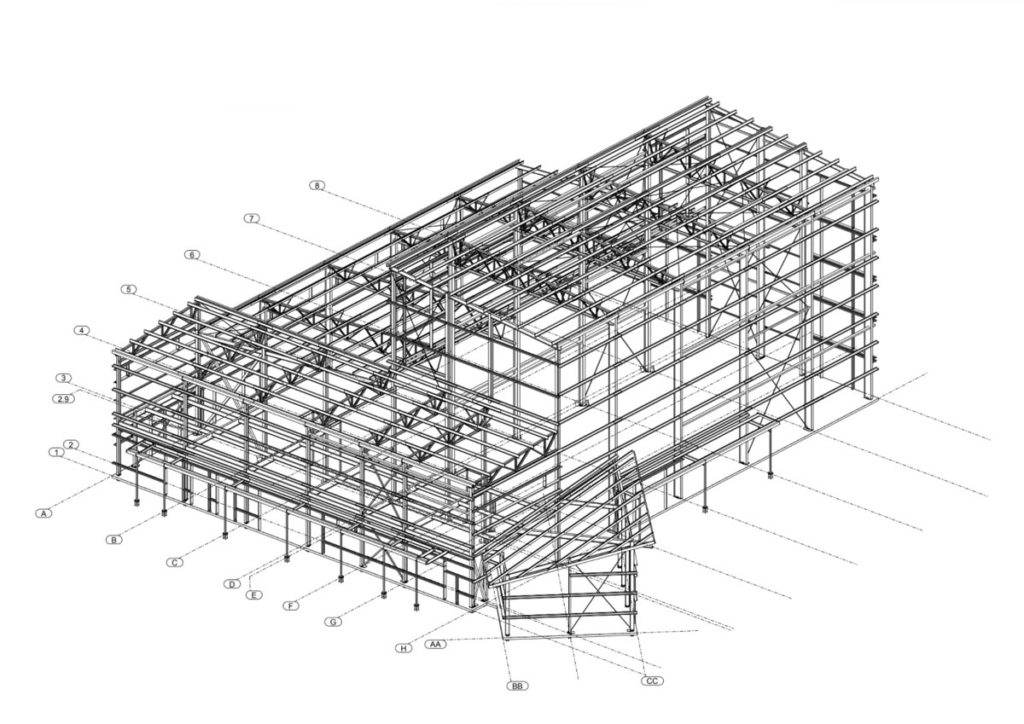
Our Hybrid Steel Buildings combine the advantages of Pre-engineered Metal Buildings (PEMBs) and Conventional Structural Steel Buildings, resulting in several notable benefits:
Cost Efficiency: Hybrid buildings leverage the precision of factory-based fabrication found in PEMBs for secondary members while benefiting from conventional steel’s structural strength. As a result, they often prove to be a more cost-effective option. These buildings minimize material waste and enhance the efficiency of production and installation processes.
Design Flexibility: Unlike PEMBs, which may have limitations in terms of design possibilities, hybrid buildings offer the same customization options as conventional steel structures. This allows for the creation of more intricate and distinctive architectural designs.
Accelerated Construction: Integrating pre-engineered components in hybrid building systems significantly reduces construction time. These components can be assembled quickly on-site, reducing the need for extensive field fabrication and expediting the construction process.
By merging the exceptional attributes of Pre-engineered Metal Buildings (PEMBs) and Conventional Structural Steel Buildings, our Hybrid Building System delivers outstanding durability, design flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and accelerated installation, rendering it an ideal selection for complex low to mid-rise new construction projects.
PEMBs and Conventional Steel Structures have distinct engineering and installation processes. PEMBs employ a pre-engineered, three-plate design, utilizing factory-cut and pre-drilled steel components for convenient assembly. They primarily use I-beams and a bolt-together system but may face challenges when dealing with complex designs.
On the other hand, Conventional Steel Buildings provide greater customization options. They utilize open web steel joists as primary members, along with field-cut and drilled I-beams, steel plates, channels, and hollow beams as secondary components. However, this flexibility results in higher labor costs and increased material usage due to on-site fabrication.
PEMBs often boast lower costs due to precise factory-based fabrication, reducing waste and production time while accelerating installation. At Western Steel, we have developed our SolutionCentric™ approach, blending these methods to create our Hybrid Building System. This system combines Conventional Steel for primary members and PEMB for secondary ones, harnessing the design flexibility of open web steel joists while maintaining the efficiency of PEMBs for optimized design flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
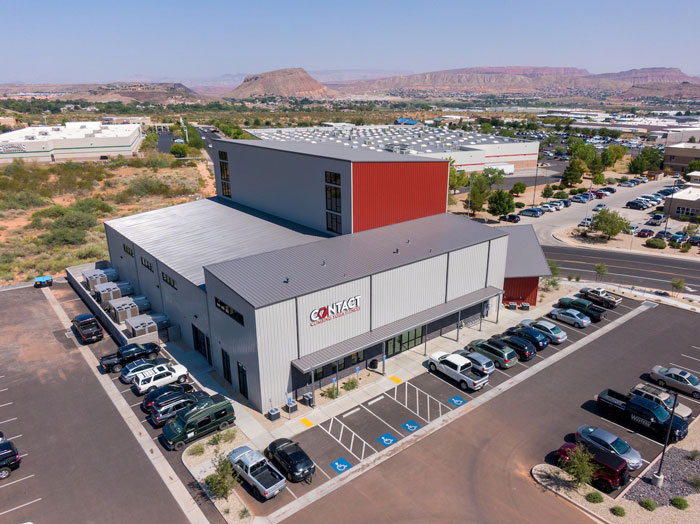

Contact Climbing St. George, UT

Open Web Steel Joists
Joists from conventional steel construction are the primary frame of a Western Hybrid Building System and they are used to support the floors or roof of a building. A steel joist must be designed to withstand forces and stress while minimizing weight, space requirements, and material costs. Different types of joist designs are available based on loading and mounting configurations. Open-web steel joist (OWSJ) consists of two parallel members, or chords, with a repeating, triangular web structure located between the chords.
Pre-Engineered Secondary Members
Secondary framing is commonly made from cold-formed steel components that meet established standards for quality and grade. The typical shapes of the secondary framing members include purlins, girts, eave struts, wall base.

Girts
A girt is a horizontal member in a wall frame that supports the wall panel. It also forms a frame around windows and doors. Purlins provide similar support for roof panels and are typically placed on top of the primary steel structure. Girts and purlins are “Z” sections, available in depths of 8, 10, or 12 inches. Each flange of the “Z” has a stiffening lip formed at a 50° angle, allowing it to connect with adjacent members and create a continuous beam across multiple sections.
Eave Struts
Are secondary members that are installed along the roof eaves to support the edge of the roofing panels. They are typically roll-formed “C” sections, 8 inches deep nominal (roll-formed) with 3 ¼ inch wide top and bottom flanges; or brake-formed “C” sections 10 inches or 12 inches deep nominal with a 3 ¼ inch wide top flange and a 4 ½ inch wide bottom flange.
Wall Base Angle Trim
Provides support for wall panels and closes off the open ribs at their base. A standard base condition is to use this one-piece member without a panel notch in the concrete foundation. However, dimensions of this member allow it to be used in conjunction with a panel notch, if the customer so desires.
MORE BUILDING OPTIONS
Our Steel Building Types Structural Pre-Engineered Hybrid

Conventional
Steel Buildings
Our Structural Engineering team streamlines each aspect of structural steel building, from design analysis to material procurement, ensuring customer satisfaction and guaranteed on-time delivery.
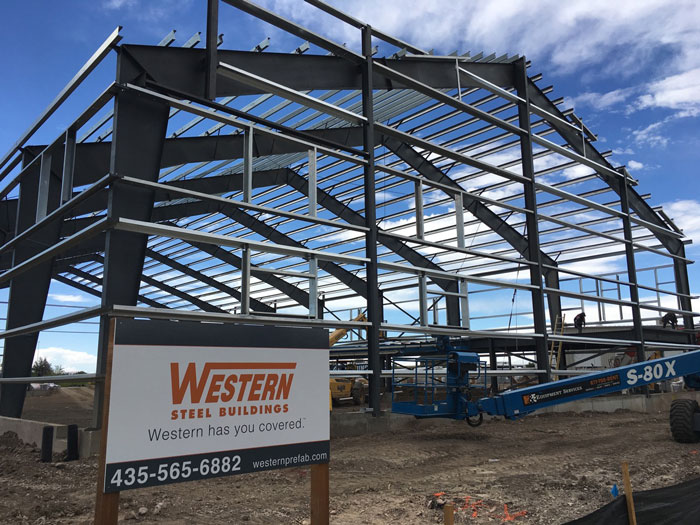

Pre-Engineered
Metal Buildings
Also known as pre-eng, this type of building system consists of precision-designed components fabricated to spec at the factory. The factory-cut, ready-to-assemble parts are then shipped to the site, speeding up the construction process.
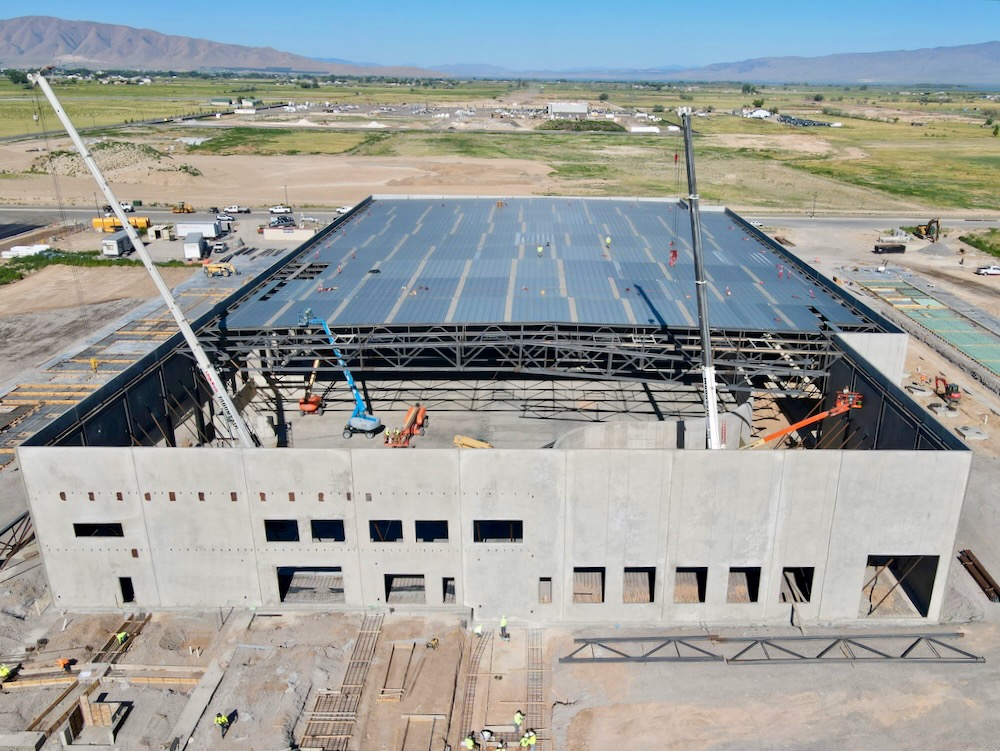

Concrete Tilt-Up
Steel Buildings
Discover the strength and versatility of our cutting-edge steel building solutions paired with the concrete tilt-up constructions. Merging the best of both worlds, we deliver unparalleled durability, design flexibility, and cost efficiency.
Areas We Serve
Our fully-integrated team of Structural Engineers, Detailers, Account Managers, and Estimators provides our clients with optimal resources for timely and cost-effective steel building solutions. This streamlined organizational structure enables us to respond quickly and complete projects within tight timeframes, ensuring timely and cost-effective results that meet even the most critical project needs.
Services Include:
Building Design & Analysis
Structural Engineering
Geotechnical Engineering
Project Management
Material Procurement
Construction Support
Building Solutions Include:
Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings (PEMB)
Conventional Steel Buildings
Hybrid Steel Buildings
Concrete Tilt-Up Steel Buildings
Services Include:
Building Design & Analysis
Structural Engineering
Geotechnical Engineering
Project Management
Material Procurement
Construction Support
Building Solutions Include:
Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings (PEMB)
Conventional Steel Buildings
Hybrid Steel Buildings
Concrete Tilt-Up Steel Buildings



